Elastic Data Connectors - Elasticsearch Ingestion Made Simple
Tech Blog
October 5, 2023 • ☕️ 4 min read
In any search application, the is an underlying ingestion pipeline that indexes the data. While developers often focus on speedy searches, they tend to overlook the aspect of data indexing. It’s important to keep in mind that easy-to-manage data ingestion is a key foundation for successful data-driven solutions.
Elasticsearch (ES) has many ingestion tools, but sometimes they don’t fit all data sources. That’s where Elastic Data Connectors come in. They let you easily link custom or proprietry data to Elasticsearch. This framework is lightweight, open-source and flexible, and works both on-premise and in the cloud. In short, it’s a straightforward way to keep any content source, e.g. database, cloud storage or local file system, in sync with a search-optimized Elasticsearch index.
Other ingestion solutions offered by the Enterprise Search component in the Elastic stack are Web Crawler and Index API.
Data Connectors Framework
The data connectors framework makes it easier for developers to create connector clients that can sync data from other sources into Elasticsearch. The framework takes care of essential tasks like scheduling data syncs, extracting text from files, and setting up index mappings automatically. This way, developers can concentrate on integrating their chosen data source without worrying about these common tasks.
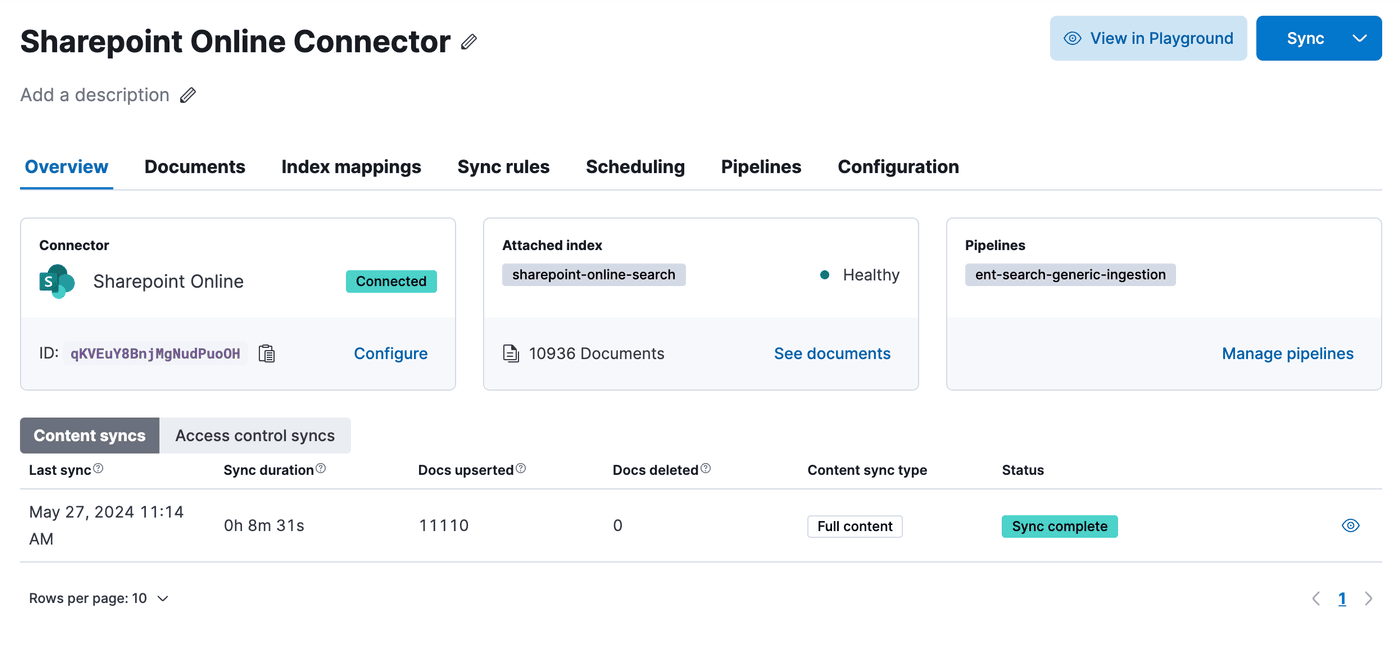
The data connectors framework can be configured to use Elasticsearch’s ingestion pipelines to perform transformations on data before storing it in an index. A common use case is document enrichment with machine learning. For example, you can:
- analyze text fields using a Text embedding model that will generate a dense vector representation of your data
- run text classification for sentiment analysis
- extract key information from text with Named Entitiy Recogintion (NER)
Architecture
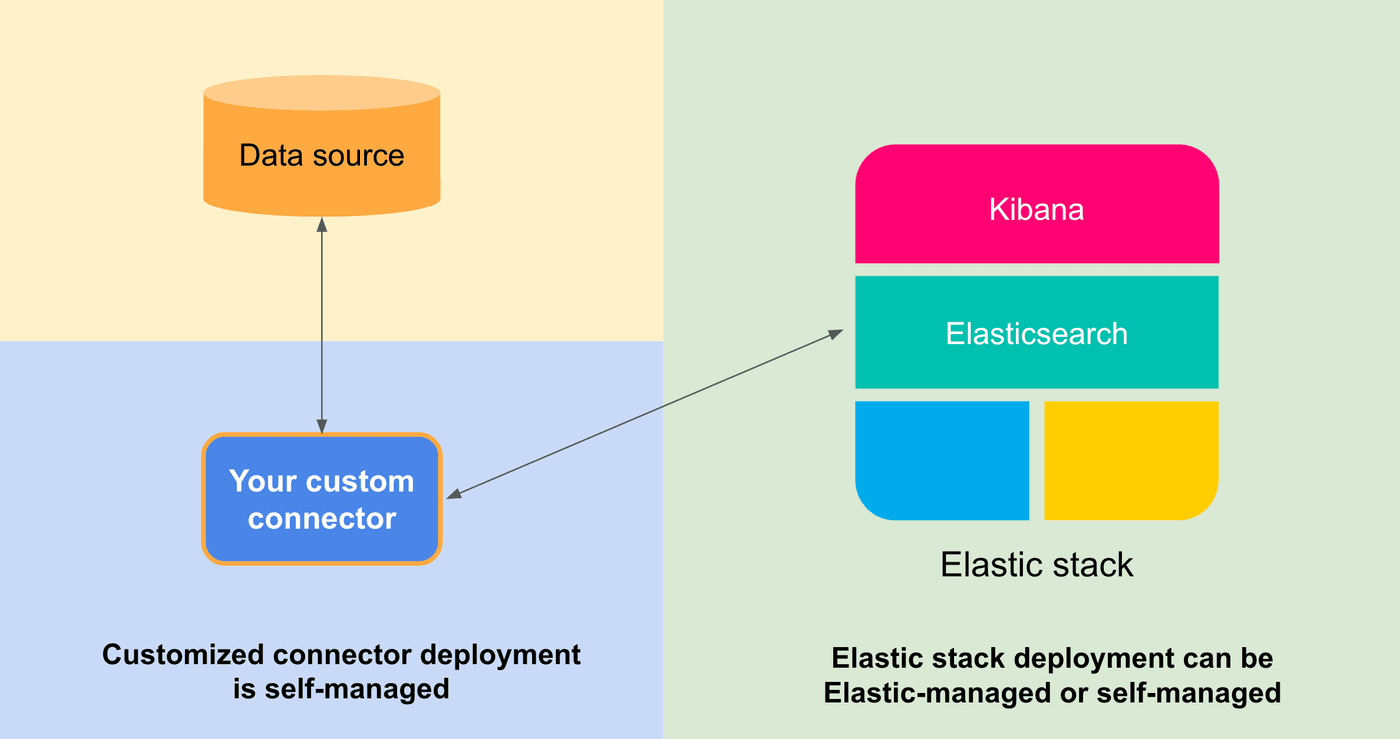
The data connectors framework is deployed as a separate stateless service. You can host them yourself, or for selected native connectors run them in the Elastic Cloud natively.
The framework connects your third-party data source with an Elasticsearch index and keeps it in sync, so that you can focus on search and analytics with your data.
Connector Protocol
Connectors framework relies on the Connector Protocol. All communication between connectors and other parts of the stack happens asynchronously through an Elasticsearch index. This comes with several benefits.
- Stateless deployment: The data connectors service relies on external state in an ES index
- Fault-tolerance: The service can resume operation on a different host after a restart or a failure. Once it reestablishes connection with Elasticsearch, it will continue its normal operation.
- Developers have control over a deployment - This service can be easily self-hosted or run in the Elastic cloud. It only needs to be able to discover your Elasticsearch instance over the network.
This setup is developer friendly and aims to make connectors service easy to deploy and manage. The framework is written in async python making this IO-bound framework lightweight, fast and efficient.
Available connectors
For an up-to-date list of supported connectors check the official documentation.
You can check the connector implementations in: connectors/sources.
Custom connectors
You are not limited to the connectors included in the data connectors framework. It is easy to implement a custom data connector using the abstractions provided by the framework.
All you need to do is define a custom DataSource class in async python and the framework will take care of making it compatible with common functionalities, such as scheduling data syncs, extracting text from files, and setting up index mappings automatically.
Here is an example starting point for implementing MyCustomDataSource. In order to turn this into a functional connector you need to define get_default_configuration, ping and get_docs methods.
class MyCustomDataSource(BaseDataSource):
"""Connector to my custom data source"""
name = "Custom Source"
service_type = "custom_source"
@classmethod
def get_default_configuration(cls):
"""Returns a dict with a default configuration"""
raise NotImplementedError
async def ping(self):
"""When called, pings the backend
If the backend has an issue, raises an exception
"""
raise NotImplementedError
async def get_docs(self, filtering=None):
"""Returns an iterator on all documents present in the backend
Each document is a tuple with:
- a mapping with the data to index
- a coroutine to download extra data (attachments)
The mapping should have least an `id` field
and optionally a `timestamp` field in ISO 8601 UTC
The coroutine is called if the document needs to be synced
and has attachments. It needs to return a mapping to index.
It has two arguments: doit and timestamp
If doit is False, it should return None immediately.
If timestamp is provided, it should be used in the mapping.
Example:
async def get_file(doit=True, timestamp=None):
if not doit:
return
return {'TEXT': 'DATA', 'timestamp': timestamp,
'id': 'doc-id'}
"""
raise NotImplementedErrorTo learn more about how to write a custom connector, refer to the How to create customized connectors for Elasticsearch blog post or check the implementation of existing connectors.
You can use Customized connector to configure and run your custom connector from Kibana. Navigate to: Search > Indices > Create a new index > Connector > Customized connector.
If you want to contribute your custom connector to the open-source connectors framework, refer to the How to contribute connectors guide in the connectors repository.